Most financial advisors and financial planners recommend to their clients some type of global asset allocation. Their global asset allocation models usually include a range of bonds, U.S. stocks, and International stocks. Some may include what are considered alternative investments like real estate (REITs), private equity, or tactical trading, but most of them keep it plain vanilla. This asset allocation method is called “strategic asset allocation” since it usually applies some form of portfolio optimization of historical returns and volatility to determine the weight between stocks and bonds.
Who can blame them? asset allocation and diversification is easy to sell and easy to defend. If someone sells their business or retires with a large 401(k), it’s easy to sell them on diversifying their assets. If the markets go down it isn’t their fault, it’s the market that’s doing it. Is it too much drawdown or volatility? They just recommend a change to less stocks and more bonds. Of course, that only works when bonds aren’t falling too.
Since many actively managed mutual funds failed to avoid losses during the last bear market 2007 to 2009, many advisors shifted their strategic asset allocation from actively managed mutual funds to index funds. It’s easy to see why; their clients lost a lot of money, even as much as -40% for a balanced portfolio of 60% stocks and 40% bonds. If they were more invested in stocks, it was as much as -50% or more.
If a mutual fund was supposed to be “active,” I can see how such losses would be unacceptable. If an investor is paying more for portfolio management, they probably expect to have a more asymmetric risk/return profile than what long-only exposure to stock indexes all the time would provide for less cost. Index funds and ETFs are cheap because they simply provide exposure to market risks and rewards. They provide this exposure all the time, so when markets fall as they do in a bear market, they lose value and have no stop loss for risk management.
I also use index ETFs to gain exposure to markets, countries, and sectors, but I don’t just buy and hold them, I increase and decrease my exposure to actively manage my risk/reward. My objective is an asymmetric risk/reward, so I want to avoid the larger losses as I try to capture gains. For me, it starts at the individual position level and flows through to the portfolio level. I’m entering positions we expect to result in an asymmetric risk/reward payoff; positions with a higher expected gain than its potential loss. I do this over and over, and they don’t all have to result in asymmetry. We just need the average gains to exceed the average losses over time to achieve a positive asymmetric risk-return profile. It’s an absolute return objective, meaning our focus is on our own payoffs and risk-reward profile, not trying to track what a stock index is doing. My strategy is unconstrained from the limitations of a fixed benchmark. Our objective is more about making money with a predetermined amount of absolute risk, not relative returns and tracking indexes. As such, the return stream is expected to be unique.
That isn’t what active mutual fund managers do.
The typical active mutual fund has an objective of relative return vs. an index benchmark. As I’ve been an investment manager for over two decades, I’ve seen the relative return comparisons become more and more intense. Brokerage firms and investment advisors have created sophisticated performance reporting programs to compare their performance to chosen benchmarks. Active mutual funds have a mandate to “beat” and index. For example, some of them aim to beat the large growth, mid value, or small growth asset classes. Most of them attempt to beat their benchmark by filtering through the stocks in the index and picking better stocks. If a relative return is their objective, they are not focused on managing downside risk. Instead, they are focused on tracking the benchmark and getting ahead of it. Many of them probably attempt it by holding a more focused portfolio or with a portfolio of the higher momentum stocks relative to the benchmark. Since risk management isn’t their objective, they view any overweight in cash as a risk of underperformance. That’s what traditional “active managers” do. What I do is typically called “tactical management” since my objective is absolute return, not relative return, and I want to actively control my drawdowns through risk management. For example, I could be positioned in all cash in a bear market, hedged, short, or long volatility.
So, there is an important distinction between “active managers” with a relative return benchmark-beating objective and those of us with an unconstrained strategy and focus on absolute returns. Mutual funds are typically relative return managers trying to beat a benchmark, hedge funds are typically absolute return managers creating their own unique return stream. Although, typically means that isn’t always the case.
Ok, so, the headline was about the performance of Global Asset Allocation this year.
Back to global asset allocation.
Some financial advisors and media enjoy disparaging all types of active management. They talk about how relative return managers like most mutual funds don’t beat their benchmarks. They’ll point out how absolute return hedge fund type strategies may manage downside risk, but don’t earn as much return as an all-stock portfolio. Most of the time, it isn’t a reasonable comparison. For example, saying the Barclays Hedge Fund Index underperformed the S&P 500 the past decade isn’t complete without also considering the drawdowns. In the last bear market, the S&P 500 declined -56% while the Barclays Hedge Fund Index that includes a composite of thousands of hedge funds declined only -24%. I will suggest the stock index loss was so large most tapped out while the Barclays Hedge Fund Index was low enough that investors could have held on.
It doesn’t matter how much the return is if the risk is so high you tap out before its achieved.
This year has been a challenging and hostile year for all investment strategies. While those who adhere to a long-only fully invested asset allocation all the time will talk about the performance of active managers, theirs isn’t much to speak of, either. I know a lot of advisors, and we work with some who invest in my portfolio. Most of their global asset allocations are very simple, and now many of them use index funds and charge an advisory fee for the asset allocation and rebalancing.
There are some mutual funds that offer a varying method of asset allocation. I am not recommending any of these funds, this is for educational and informational purposes only. Some popular ones that come to mind are BlackRock Global Allocation (MDLOX), Arrow DWA Balanced. PIMCO All Asset All Authority (PAUAX), DFA Global Allocation 60/40 (DGSIX). BlackRock Global Allocation, Arrow DWA Balanced, and PIMCO All Asset All Authority are active allocation funds while DFA Global Allocation is a passive allocation fund managed by Dimensional Fund Advisors. Below are their year-to-date total returns, including dividends. (To see their full history click on the links in their names above.)

I know financial advisors who are big advocates of large asset managers like Dimensional Fund Advisors (DFA), PIMCO, and BlackRock. Advisors often tout how large they are and how many academics or how many analysts and portfolios managers they have on staff. I included the Arrow DWA Balanced fund because it’s managed by Dorsey Wright, which isn’t as large, but I know advisors use it. Most advisors who offer asset allocation models are doing their own asset allocations for their clients. The above returns are the result of each of these asset managers doing the allocation and investment selection. So, I would expect when it comes to global asset allocation, those funds should be as good as it gets. How is a financial planner who isn’t a portfolio manager going to do better?
Some may say “What about Vanguard? They are some of the cheapest funds you can buy?”. I don’t know of a Vanguard global asset allocation fund like the DFA fund, but they do have a balanced 60/40 fund that doesn’t include exposure to international. Below is their balanced allocation fund along with their International stock fund. Though their fund isn’t down -7% like the global allocation funds, if you added 20% of their International to make it “global,” we can see it would be similar.

Since indexing and ETFs have become more popular than mutual funds, today we have some interesting ETFs that track global asset allocation indexes so we can better understand the return streams of global asset allocation.
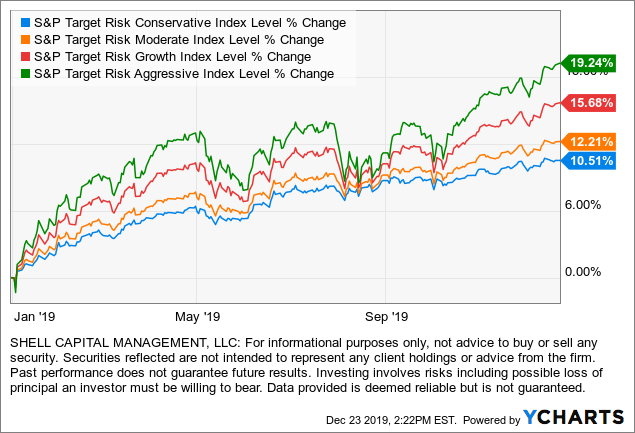
iShares is a BlackRock company, the world’s largest asset manager with $6.29 trillion in assets under management. If an investor thinks a large size with many professionals is the key to investment success, they would probably BlackRock is the best. Of course, I don’t agree, since the most skilled portfolio managers I know are small, focused, specialized firms with all their skin in the game. BlackRock’s iShares offers the iShares Core Allocation Funds, which are ETF allocations of ETFs. Each iShares Core Allocation Fund offers exposure to U.S. stocks, international stocks, and bonds at fixed weights and holds an underlying portfolio of iShares Core Funds. Investors can choose the portfolio that aligns with their specific risk considerations like investment time horizon and risk tolerance; for example, those with longer investment time horizons and higher risk tolerance may consider the iShares Core Aggressive Allocation ETF.
More specifically, the iShares Core Allocation Funds track the S&P Target Risk Indexes. So, not only do you have BlackRock’s portfolio management managing the fund, but they are tracking S&P Target Risk Indexes. Here is their description:
S&P Dow Jones Indices’ Target Risk series comprises multi-asset class indices that correspond to a particular risk level. Each index is fully investable, with varying levels of exposure to equities and fixed income and are intended to represent stock and bond allocations across a risk spectrum from conservative to aggressive.
In other words, they each provide varying allocations to bonds and stocks. The Conservative model is more bonds, the Aggressive model is more stocks.
S&P Target Risk Conservative Index. The index seeks to emphasize exposure to fixed income, in order to produce a current income stream and avoid excessive volatility of returns. Equities are included to protect long-term purchasing power.
S&P Target Risk Moderate Index. The index seeks to provide significant exposure to fixed income, while also providing increased opportunity for capital growth through equities.
S&P Target Risk Growth Index. The index seeks to provide increased exposure to equities, while also using some fixed income exposure to dampen risk.
S&P Target Risk Aggressive Index. The index seeks to emphasize exposure to equities, maximizing opportunities for long-term capital accumulation. It may include small allocations in fixed income to enhance portfolio efficiency.
Below is an example of the S&P Target Risk Index allocations and the underlying ETFs they invest in. Notice their differences is the 10% to 20% allocation between stocks and bonds.

These ETFs offer low-cost exposure to global asset allocation with varying levels of “risk,” which really means varying levels of allocations to bonds. I say they are “low-cost” because these ETFs only charge 0.25% including the ETFs they are invested in. Most financial advisors probably charge 1% for global asset allocation, not including trade commissions and the fund fees they invest in. Even the lowest fee advisors charge at least 0.25% plus the trade commissions and the fund fees they invest in. With these funds, investors who want long-only exposure all the time to global stock and bond market risks and returns, they can get it cheap in one fund.
Now that we know what they are, below are their total returns including dividends year to date in 2018. (To see the full history click: iShares)

The % off high chart shows their drawdowns from their price high.

Global asset allocation is having a challenging year in 2018 because U.S. stocks, International stocks, and bonds are all down this year.
Of course, a calendar year doesn’t mean a lot. What we do over 15 or 20 years or more is what matters. But, as low-cost index asset allocation advisors talk about the performance of active managers and hedge fund type managers, 2018 has included conditions that have been hostile for all kinds of strategies.
As I said yesterday if this market volatility and correction develops into a full bear market, the asset allocations that are fully exposed to downside risk will test investors’ tolerance for drawdowns.
How deep can drawdowns be for such a globally diversified portfolio? Looking at the historical % off high of DFA Global Allocation and Vanguard Balanced gives a historical example. Even two of the efficient allocation funds available had drawdowns of around -35% to -40% in the last bear market. If it’s done it before, it can certainly happen again.

Those of us applying active risk management and hedging strategies aim to limit the drawdowns within a tolerable amount rather than allowing them to become too large. For me, more than -20% becomes exponentially more difficult to tolerate and recover from. We have to deal with the -10% or so drawdowns sometimes since we can’t avoid them all. We necessarily have to take some risk to gain exposure to the possibility of gains.
Ok, so my headline was a little exaggerated. Drawdowns of -5% to -12% isn’t exactly a “beating”, but that’s the kind of headline we often see about active management and hedge funds.
You can probably see why I believe it’s essential to actively manage risk and position capital in the direction of price trends.
Mike Shell is the Founder and Chief Investment Officer of Shell Capital Management, LLC, and the portfolio manager of ASYMMETRY® Global Tactical.
The observations shared on this website are for general information only and are not specific advice, research, or buy or sell recommendations for any individual. Investing involves risk including the potential loss of principal an investor must be willing to bear. Past performance is no guarantee of future results. The presence of this website on the Internet shall in no direct or indirect way raise an implication that Shell Capital Management, LLC is offering to sell or soliciting to sell advisory services to residents of any state in which the firm is not registered as an investment advisor. Use of this website is subject to its terms and conditions.





















































































 In contrast, the Dow Jones Industrial Average is up about 1% over the same period – counting dividends. You may be wondering what is causing this divergence? Below is the sector holdings for the
In contrast, the Dow Jones Industrial Average is up about 1% over the same period – counting dividends. You may be wondering what is causing this divergence? Below is the sector holdings for the  The position size matters and makes all the difference. Notice in the table above the Utilities, Consumer Staples, and Energy Sectors are the top holdings of the index. As you see below, the Utilities sector is down nearly -9% year-to-date, Energy and Staples are down over -1%. They are the three worst performing sectors…
The position size matters and makes all the difference. Notice in the table above the Utilities, Consumer Staples, and Energy Sectors are the top holdings of the index. As you see below, the Utilities sector is down nearly -9% year-to-date, Energy and Staples are down over -1%. They are the three worst performing sectors… Source: Created by ASYMMETRY® Observations with
Source: Created by ASYMMETRY® Observations with 



















You must be logged in to post a comment.